In our new series, short summaries of recent D1 publications by Semmelweis University’s reaseachers will be available on a regular basis. A journal is assigned to be in D1 (first decile) if it ranked within the first 10% of journals within its subject area. The papers are selected by the Central Library and Dr. Gyula Szigeti, Director of Innovation.
Implanted device demonstrates in vivo the spread of inflammatory response to the local network of mast cells via mast cell-derived extracellular vesicles
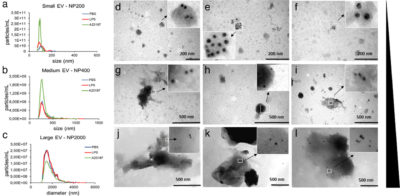 Mast cells are essential immune cells that effectively take part in the fight against pathogens. Based on the summary of Dr. Krisztina Vukman Visnovitzné, research fellow at the Department of Genetics, Cell- and Immunobiology, the study focuses on the mast cells of GFP-transgenic mice, whose mast cells contain fluorescent protein in the cytoplasm. Diffusion chambers were implanted in the peritoneal cavities of the mice and extracellular vesicles (EVs, which are membrane coated particles) that were produced by the chambers were released into the peritoneal cavity of the animal, unlike the cells, which remained in the chamber. This way, the effectiveness of mast cell-derived extracellular vesicles were studied in vivo for the first time. It was demonstrated that the extracellular vesicles, released through the pores of the chamber’s membrane into the peritoneal cavity were primarily taken up by local mast cells. If the mast cells had been exposed to inflammatory stimuli before implantation in the chamber, the vesicles they released induced the production of TNFα (tumor necrosis factor alpha) cytokine in the peritoneal cavity. The results published in the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles and the in vivo experimental system demonstrated that a small number of mast cells in certain local compartments of a living organism are able to set up a network-like communication system with the help of EVs. This way, they are able to extend the proinflammatory response that is essential in defense against pathogens. The research results and the system presented in the paper enable the study of mast cells and the extracellular vesicles produced by cells implanted in a chamber in a living organism.
Mast cells are essential immune cells that effectively take part in the fight against pathogens. Based on the summary of Dr. Krisztina Vukman Visnovitzné, research fellow at the Department of Genetics, Cell- and Immunobiology, the study focuses on the mast cells of GFP-transgenic mice, whose mast cells contain fluorescent protein in the cytoplasm. Diffusion chambers were implanted in the peritoneal cavities of the mice and extracellular vesicles (EVs, which are membrane coated particles) that were produced by the chambers were released into the peritoneal cavity of the animal, unlike the cells, which remained in the chamber. This way, the effectiveness of mast cell-derived extracellular vesicles were studied in vivo for the first time. It was demonstrated that the extracellular vesicles, released through the pores of the chamber’s membrane into the peritoneal cavity were primarily taken up by local mast cells. If the mast cells had been exposed to inflammatory stimuli before implantation in the chamber, the vesicles they released induced the production of TNFα (tumor necrosis factor alpha) cytokine in the peritoneal cavity. The results published in the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles and the in vivo experimental system demonstrated that a small number of mast cells in certain local compartments of a living organism are able to set up a network-like communication system with the help of EVs. This way, they are able to extend the proinflammatory response that is essential in defense against pathogens. The research results and the system presented in the paper enable the study of mast cells and the extracellular vesicles produced by cells implanted in a chamber in a living organism.
Krisztina V. Vukman, Andrea Ferencz, Daniella Fehér, Krisztina Juhos, Péter Lőrincz, Tamás Visnovitz, Anna Koncz, Krisztina Pálóczi, Gábor Seregélyes, András Försönits, Delaram Khamari, Alicia Galinsoga, László Drahos, Edit I. Buzás
J Extracell Vesicles. 2020; 10:e12023. https://doi.org/10.1002/jev2.12023