Long-term survival following upgrade compared with de novo cardiac resynchronization therapy implantation: a single-centre, high-volume experience
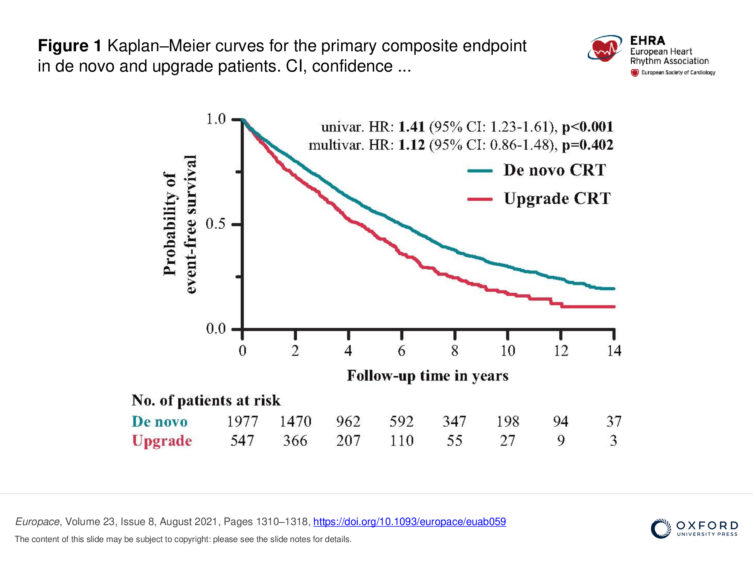 Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is an effective treatment in symptomatic heart failure (HF) patients. The study compared the results of two groups of patients undergoing CRT procedures. “De novo” patients received their first implanted devices, while the second group consisted of patients whose previously implanted devices (pacemakers, cardioverter-defibrillators) got updated to a CRT device. Regarding the baseline clinical characteristics, upgrade patients were significantly older, suffered more frequently from other diseases compared to de novo patients. Females were less common in the upgrade patient group.
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is an effective treatment in symptomatic heart failure (HF) patients. The study compared the results of two groups of patients undergoing CRT procedures. “De novo” patients received their first implanted devices, while the second group consisted of patients whose previously implanted devices (pacemakers, cardioverter-defibrillators) got updated to a CRT device. Regarding the baseline clinical characteristics, upgrade patients were significantly older, suffered more frequently from other diseases compared to de novo patients. Females were less common in the upgrade patient group.
“During the median follow-up time of 3.7 years we demonstrated a 41% higher risk of mortality in upgrade compared to de novo patients. Further analysis has found that the “upgrade” intervention is not an independent predictor of mortality. The higher mortality rates in the upgrade group may be attributable to the higher comorbidity burden of upgrade patients. The rate of peri- and post-procedural complications (i.e. lead dysfunction and pocket infections) was higher among upgrade patients than in the de novo group,” – added Walter Richárd Schwertner, student of the Doctoral School of Theoretical and Translational Medicine.
Long-term survival following upgrade compared with de novo cardiac resynchronization therapy implantation: a single-centre, high-volume experience
Walter Richard Schwerner (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Anett Behon (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Eperke Dóra Merkely (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Marton Tokodi (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Attila Kovacs (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Endre Zima (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Istvan Osztheimer (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Levente Molnar (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Akos Kiraly (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Roland Papp (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Laszlo Geller (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Luca Kuthi (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Boglarka Veres (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Annamaria Kosztin (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University), Bela Merkely (Heart and Vascular Centre, Semmelweis University)
EP Europace (2021), Volume 23, Issue 8, Pages 1310–1318.


