A video demonstrates the proper way of putting on and taking off personal protective equipment and detailed information is provided on the differences between respiratory masks and their proper use.
Information on respiratory protection:
Surgical masks
They should be used primarily by those who want to protect their environment form the drops and pathogens that they could exhale or transmit by coughing. The duration of their use cannot be determined in hours. They need to be replaced as soon as they get wet, as wet environments are hotbeds for pathogens, thus increasing the risk of infection.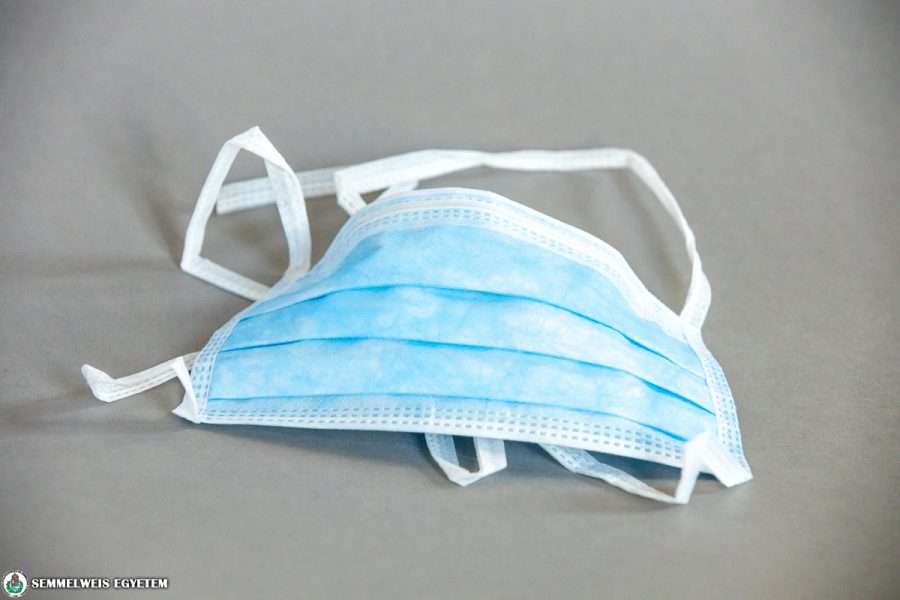
Respirators and dust masks: particulate filtering masks (FFP1, FFP2, FFP3)
They are designed to reduce the inhalation of airborne contaminants for the person to be protected, to levels that are not harmful to health. Protection is not 100% due to the so-called “inward leakage”. Manufacturers should indicate the Nominal Protection Factor (NPF), which is the coefficient of the occupational exposure limit and the inward leakage of the protective mask. This is an informative data which allows the manufacturer to advise users on what level of concentration the equipment can be safely used. There are three levels of protection: FFP1, FFP2 and FFP3. Protective capability is the greatest of the masks labelled with number 3.
In health care, the duration of its use lasts for a single intervention. The mask then should be disposed of. It is recommended for those in contact with people suspected of infection to wear disposable FFP2 and FFP3 particle filtering masks.
The efficiency of the mask is determined by the amount of inward leakage, therefore, its proper adjustment on the face is important:
- The face should be shaved, as the beard and other facial hair can prevent the face and the edge of the mask from touching.
- Long hair should be tied up at the back.
What needs special attention when putting on respiratory protective mask?
- Place the upper strap on the top of your head. Adjust the twisted strap.
- Shape the nose guard following the contours of the nose and the face for a secure seal.
- In case of masks WITHOUT VALVES, exhale strongly. In case of masks WITH VALVES, inhale deeply.
- If air flows around the nose, re-adjust the nose part.
- If air is escaping around the edges of the mask, flatten the straps around the head.
- In case of panel masks, make sure that all panels are turned outside and not inside.
- Place the lower strap under the ear making sure that the strap is not twisted.
The proper use of the personal protective equipment
While putting on and taking off personal protective equipment, the risk of infection among health care workers and patients can be reduced by complying with the guidelines of the WHO. Semmelweis University’s video demonstrates the proper use of personal protective equipment. (Video is available only in Hungarian)
Photo: Attila Kovács – Semmelweis University
Video: László Sturbán, Attila Kovács– Semmelweis University