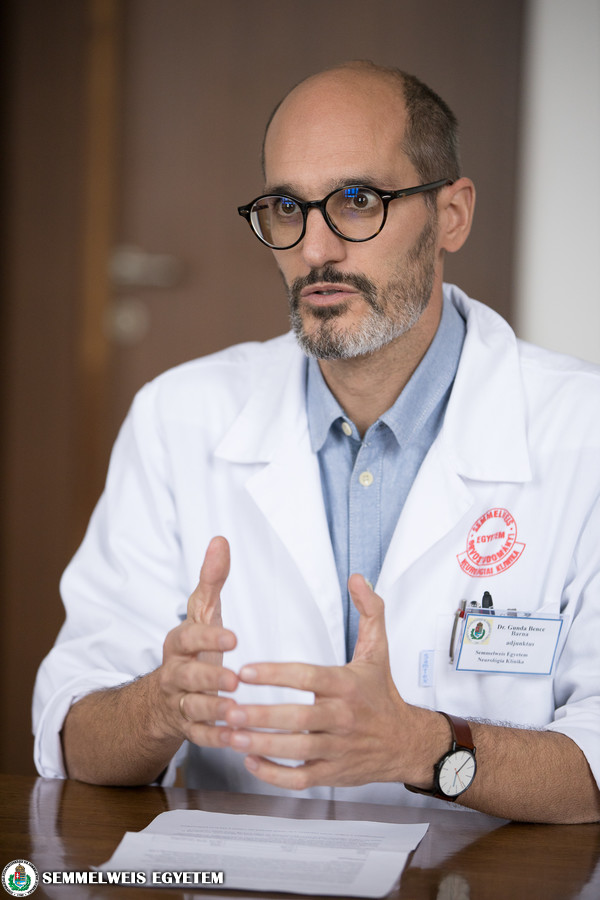
“The Department of Neurology of Semmelweis University has performed exceptionally well for years in the voluntary quality assurance of European stroke departments (Angels initiative), received gold and platinum medals, therefore we had an opportunity in 2018 to try out an artificial intelligence (AI) based software for stroke treatment (E-Stroke Suite, Brainomix, UK) for 7 months, which further improved patient care,” said Dr. Bence Gunda, senior lecturer at the department. The results were also presented in a brief study by Dr. Gunda at a Hungarian Society of Neuroradiology conference in November.
“The Department of Neurology of Semmelweis University has performed exceptionally well for years in the voluntary quality assurance of European stroke departments (Angels initiative), received gold and platinum medals, therefore we had an opportunity in 2018 to try out an artificial intelligence (AI) based software for stroke treatment (E-Stroke Suite, Brainomix, UK) for 7 months, which further improved patient care,” said Dr. Bence Gunda, senior lecturer at the department. The results were also presented in a brief study by Dr. Gunda at a Hungarian Society of Neuroradiology conference in November.
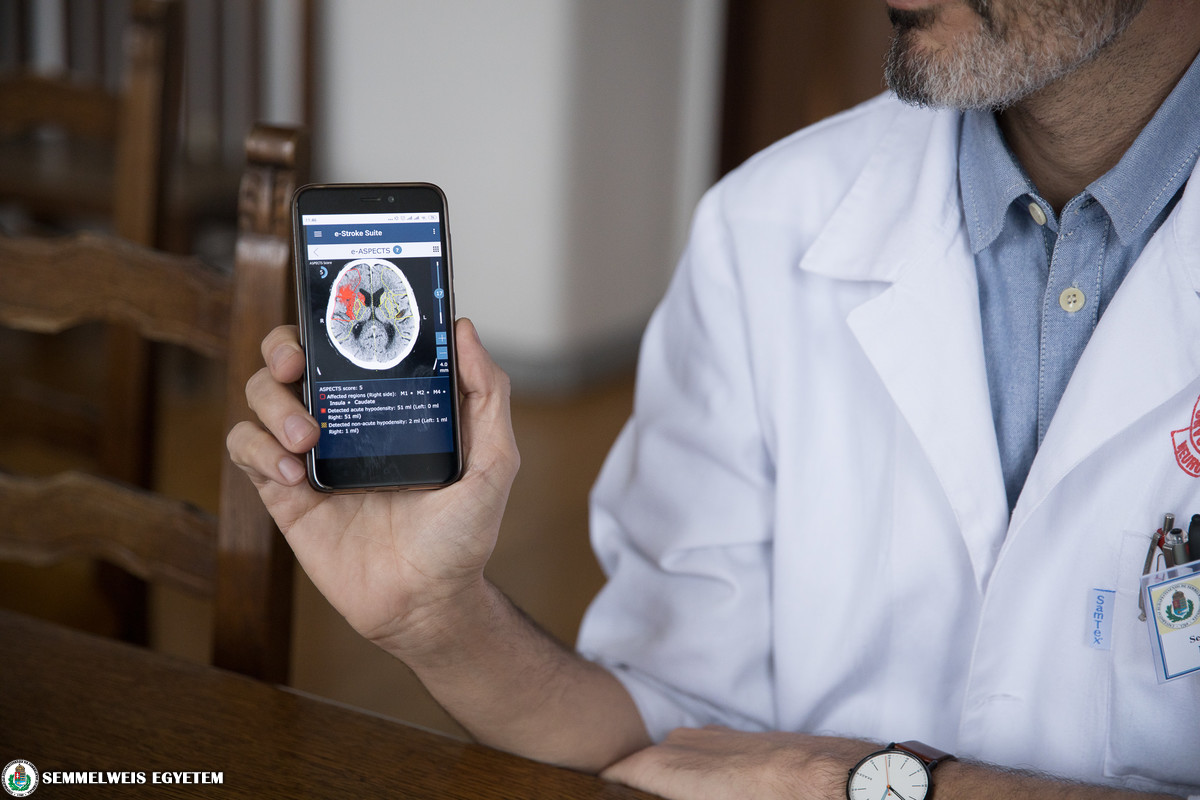
As the senior lecturer noted, acute ischemic stroke patients require quick and multidisciplinary action, meaning that difficult and complex decisions need to be made quickly, ideally within 30-60 minutes of arrival at the hospital. The more time passes, the less the chance of recovery is for patients, so in this situation it is a great help to have an AI-based system that helps decisionmaking, not by making a diagnosis but by supporting the work of physicians, said Dr. Gunda. The software works by analyzing the patient’s CT scan in 30 seconds, identifying the exact area where the damage is, its size, where the blockage is and how much brain tissue can be saved. “The same would take a neurologist or radiologist 10 minutes, and the evaluations could differ from doctor to doctor,” noted the expert. The results can also be shared immediately online or on a smartphone, so specialists even in another institute can access it at once.
Dr. Gunda revealed that from 2017 to 2018 at the department, the number of drug treatments for blood clots in the brain increased by 57% in the period, and the average time of treatment also decreased from 44 to 41 minutes. The number of endovascular (catheter) treatments also grew by 71%. “So use of the software clearly improved patient care , which is why we hope that we it will become available to use in the future as well on a daily basis as well as for research purposes,” said Dr. Gunda. Regarding future plans, he said that they are preparing further cooperation with the company developing the software to conduct a clinical study on which imaging parameters could help predict stroke progression, as well as moving to MR-based acute treatment and conducting catheterized blood clot treatment at Semmelweis University, making it a center of stroke treatment in Hungary.
Keresztes Eszter
Eszter Keresztes
Translation: Tamás Deme
Photo: Attila Kovács – Semmelweis University