Old protocol accuracy results
Accuracy results about IOSs tested before 2023 September according to the old protocol.
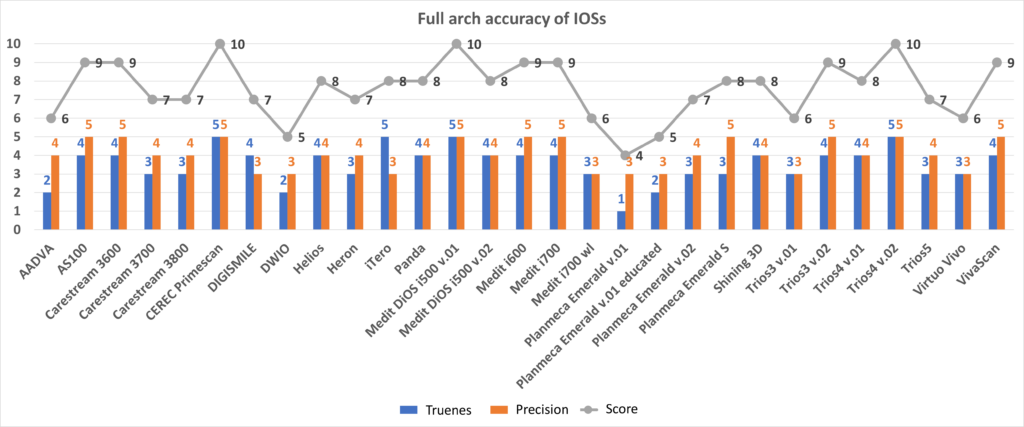
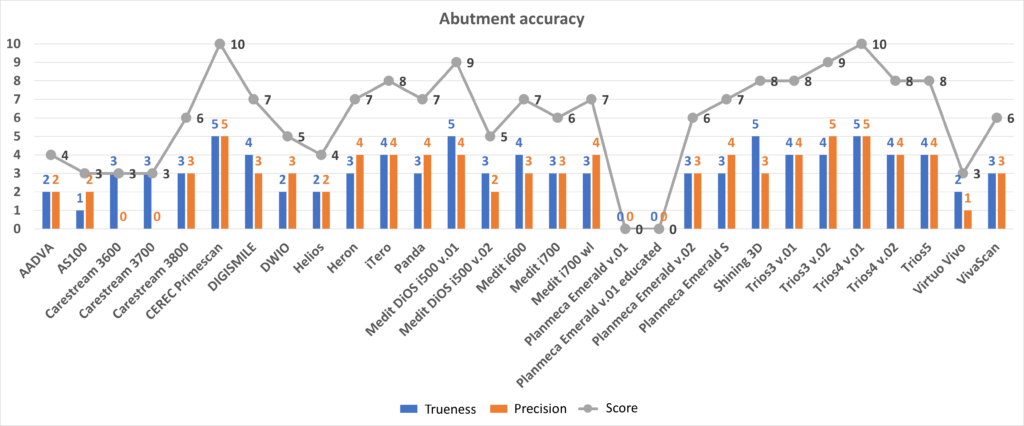
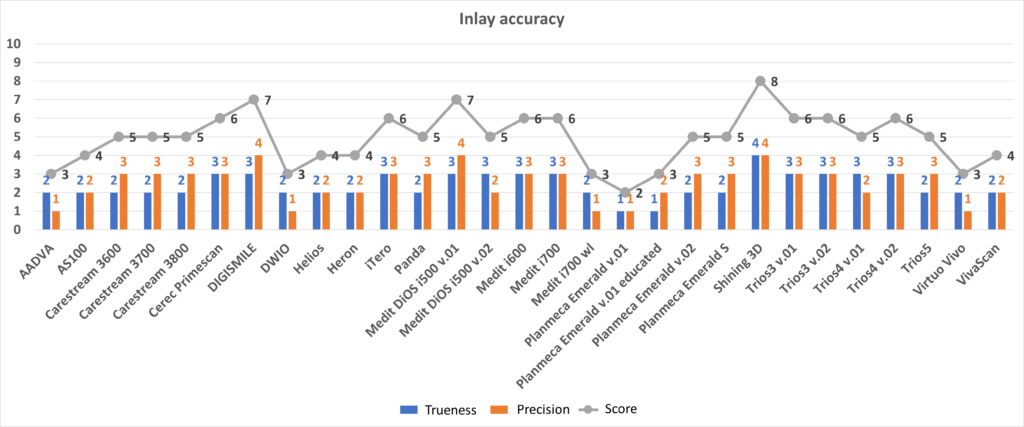
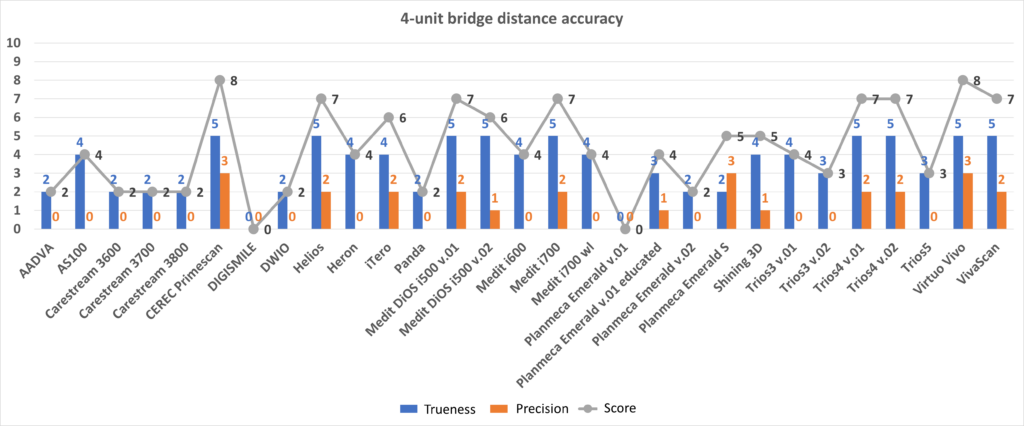
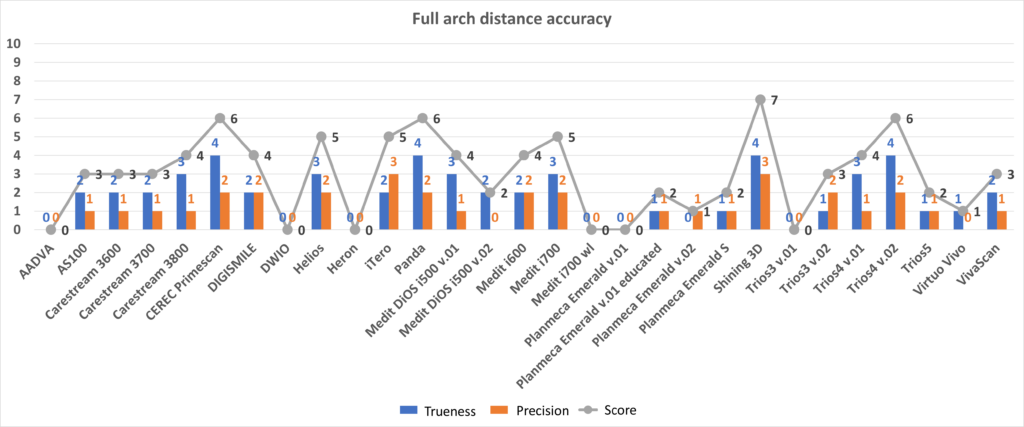
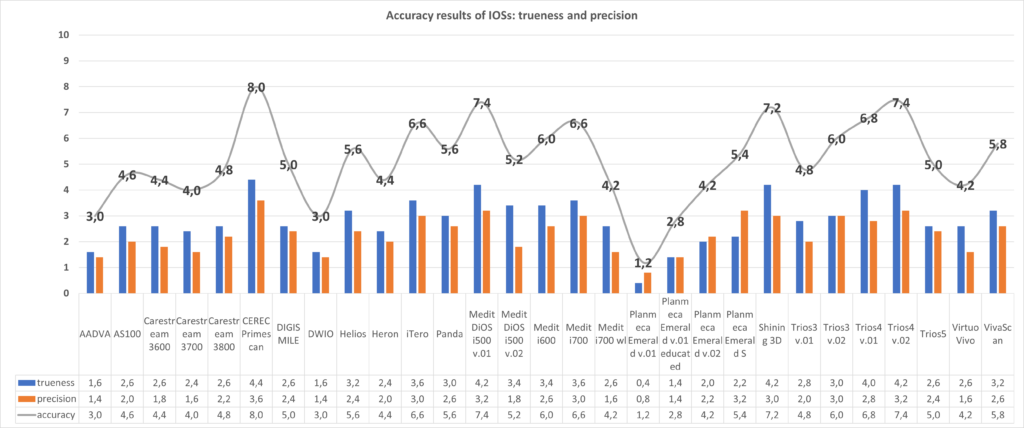
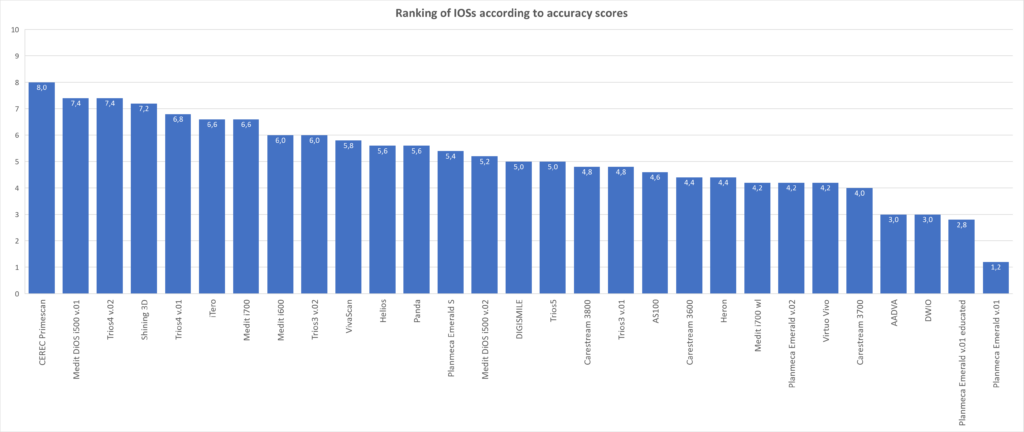
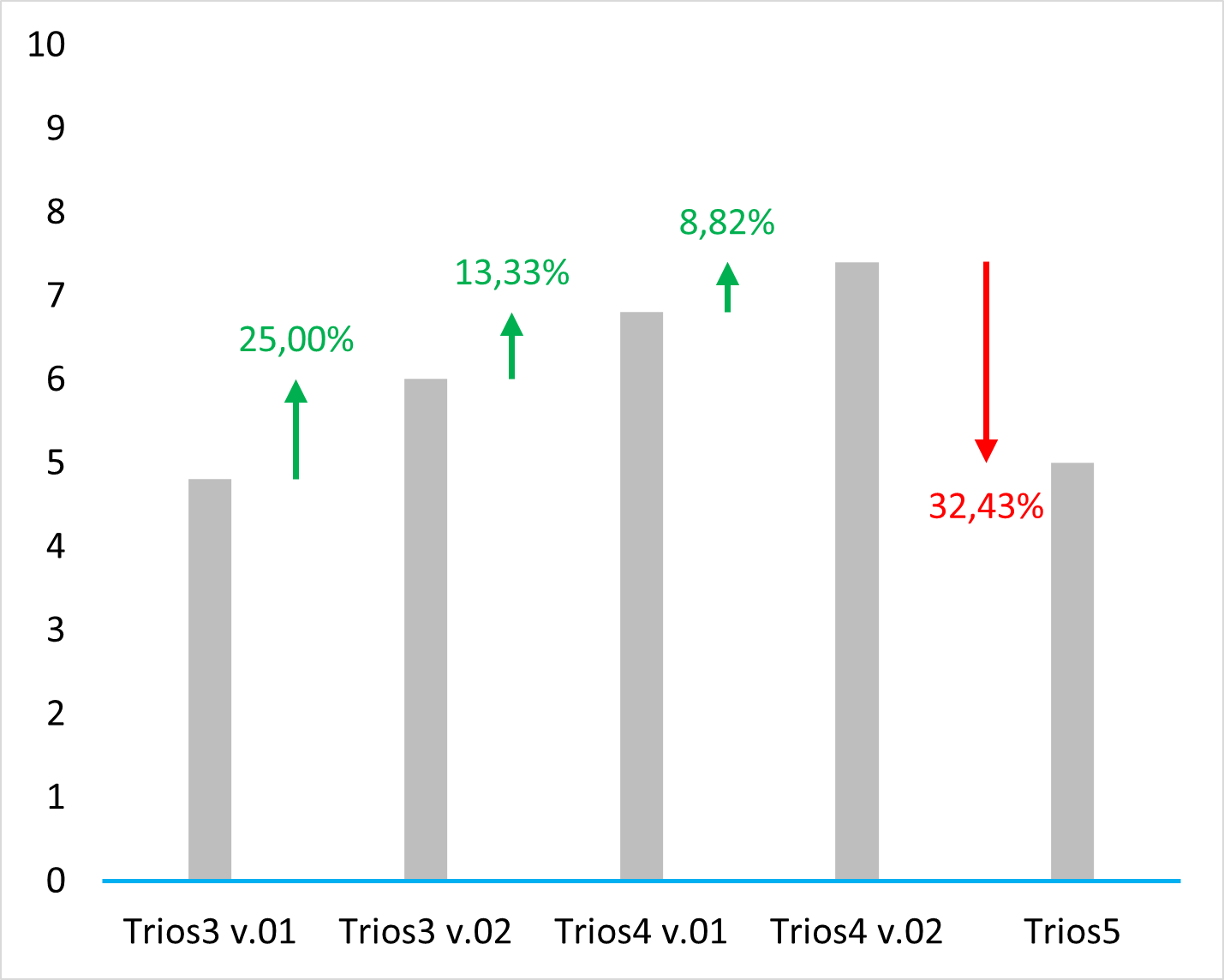
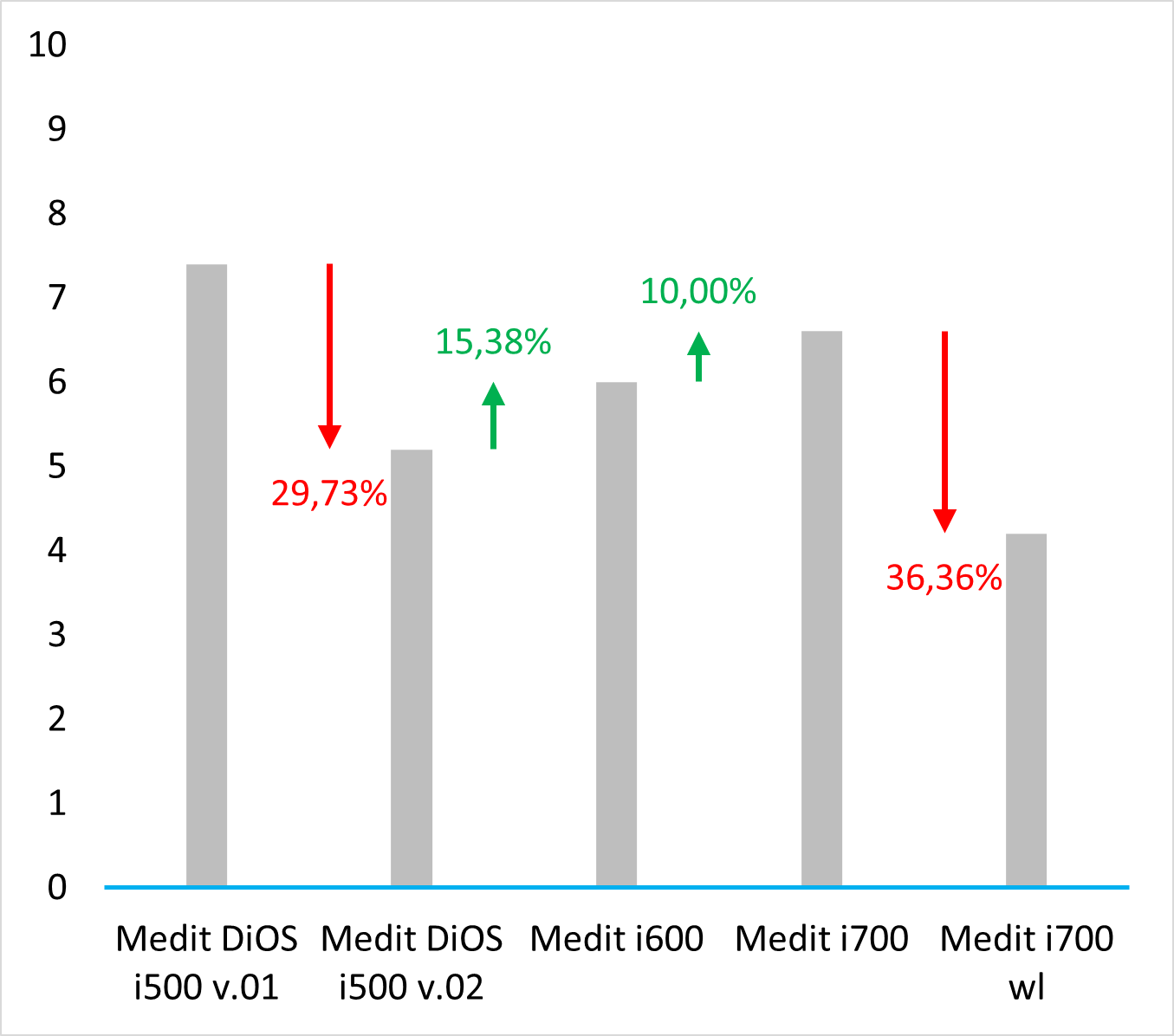
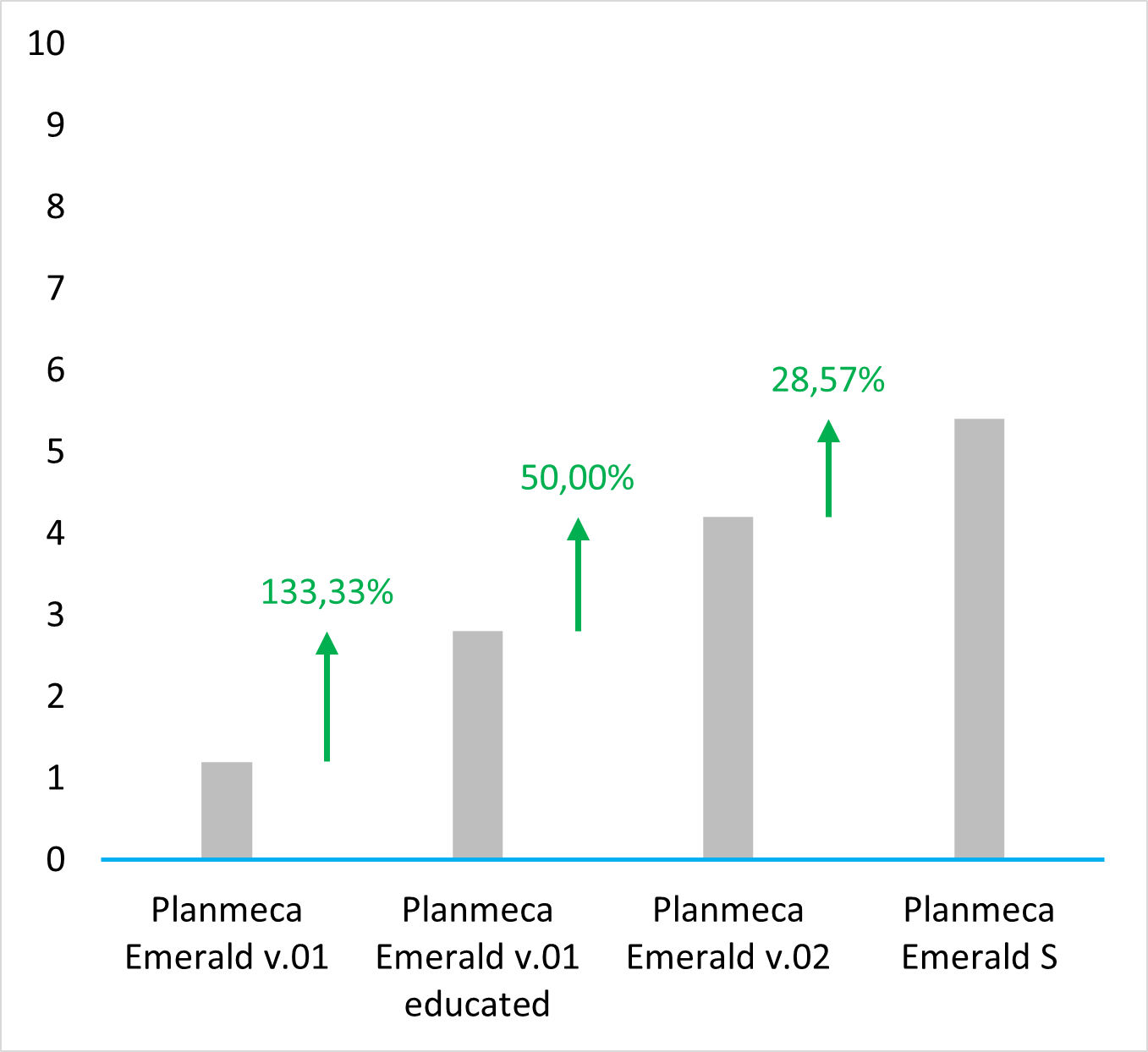
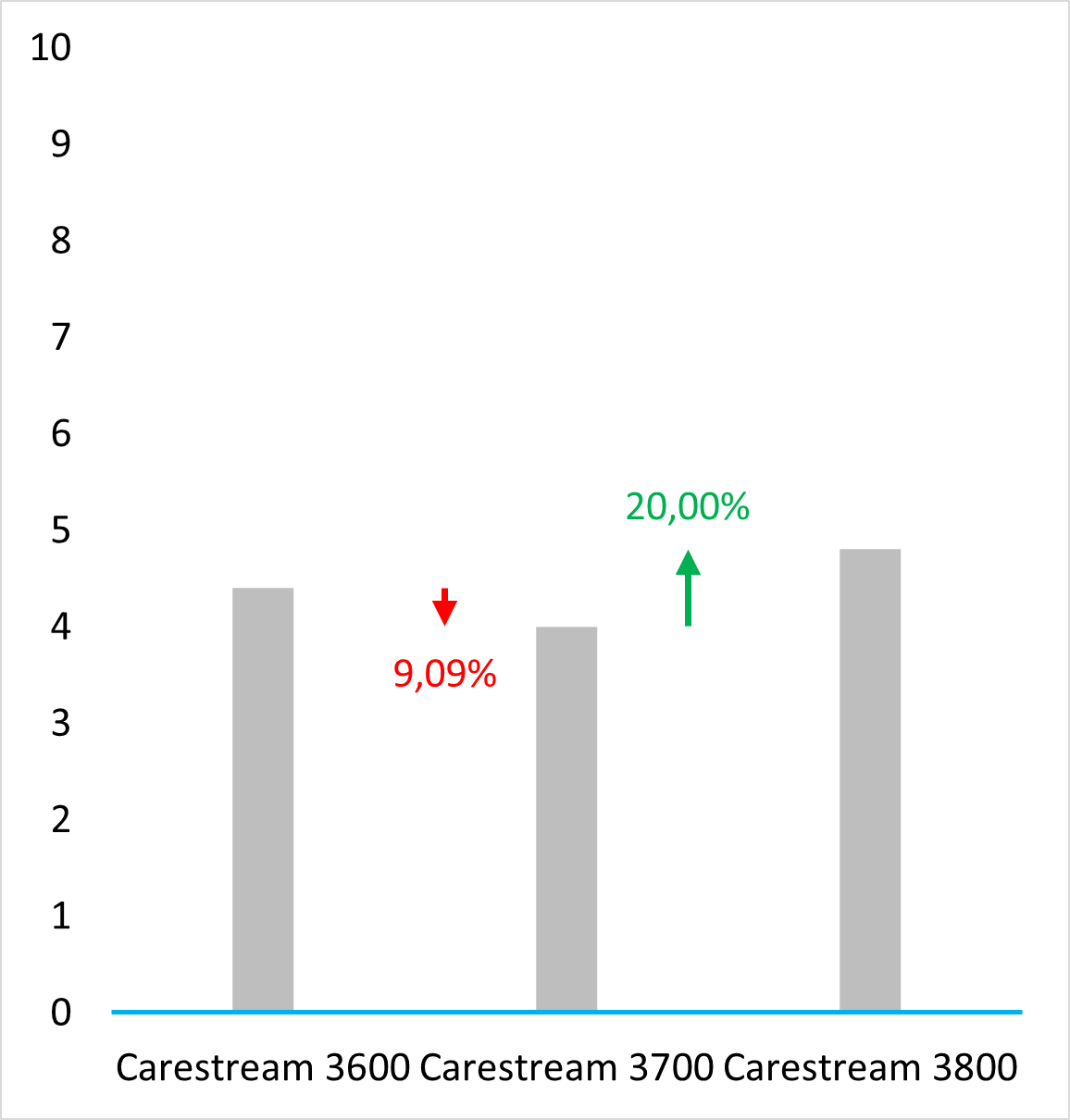
https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-023-02926-y
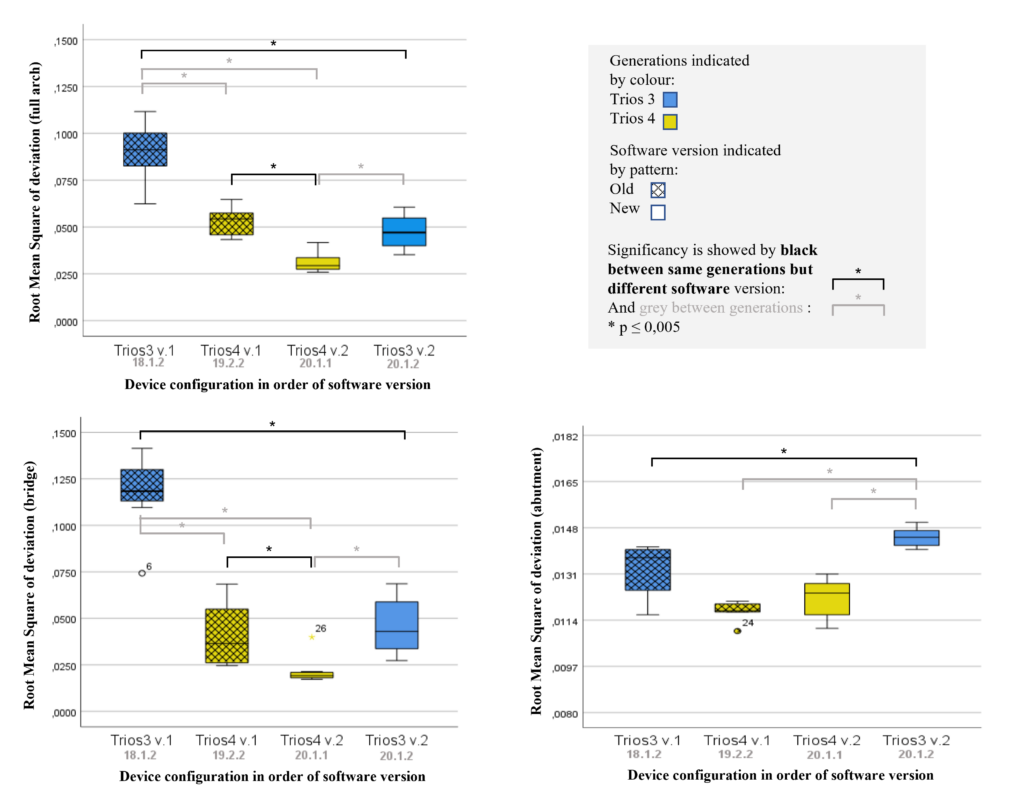
https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-023-02926-y
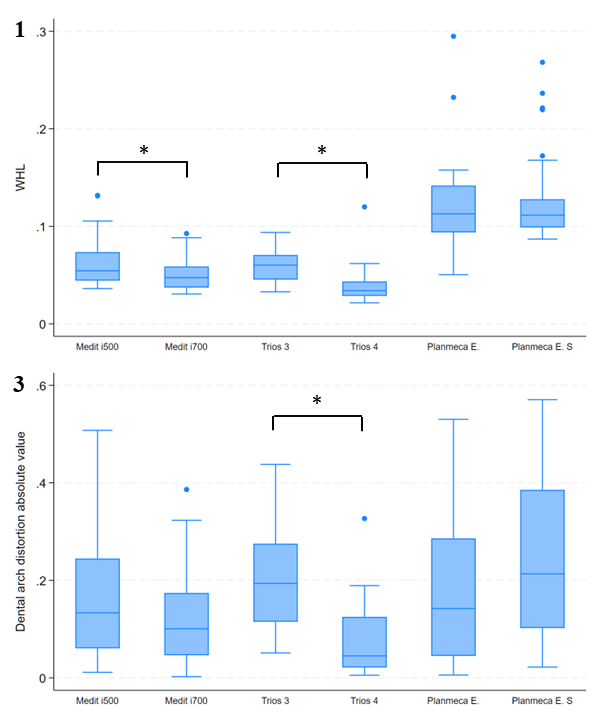
https://bmcoralhealth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12903-023-03476-z
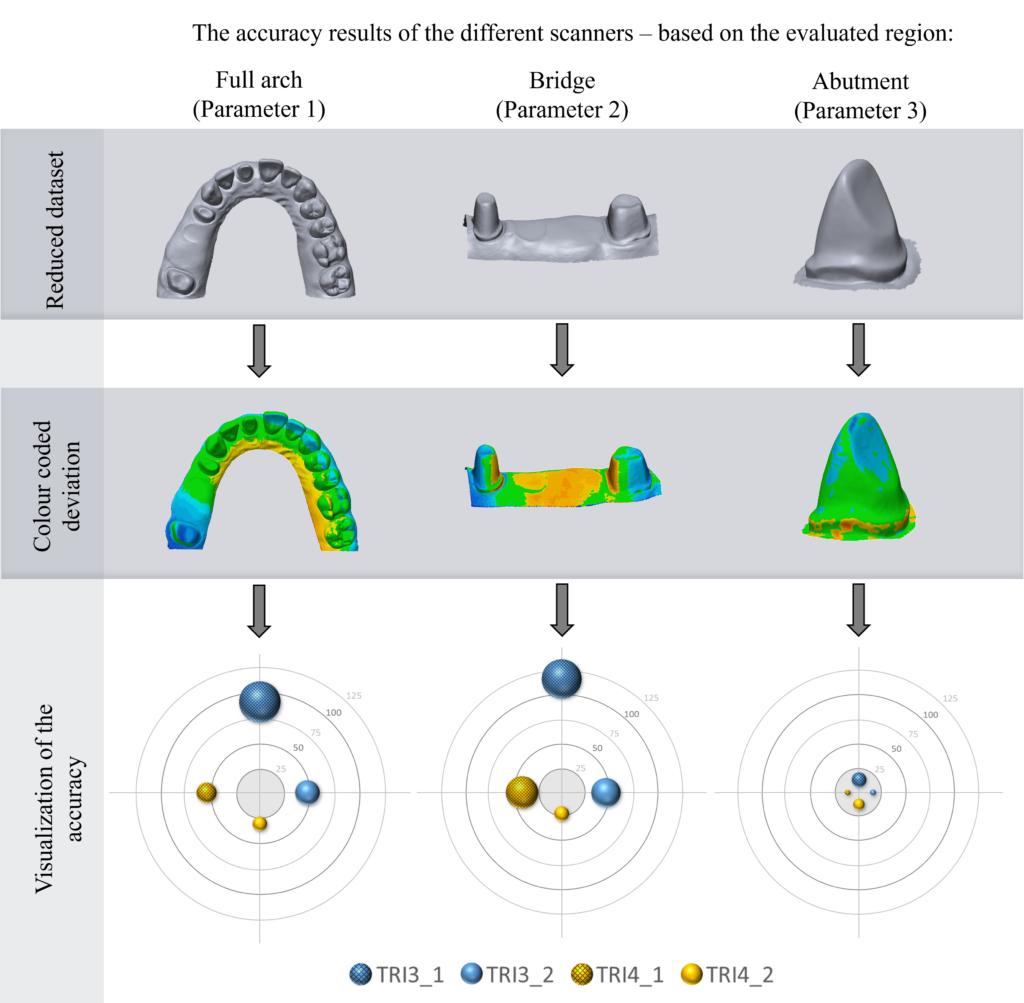
New protocol accuracy results
Accuracy results about IOSs tested after 2023 September according to the new protocol.